BAPI
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
BAPI interview preparation
Interface(BAPI) are standardized programming interfaces (methods) enabling external applications to access business processes and data in the R/3 System.
They provide stable and standardized methods to achieve seamless integration between the R/3 System and external applications, legacy systems and add-ons.
BAPIs are defined in the BOR(Business object repository) as methods of SAP business object types that carry out specific business functions.They are implemented as RFC-enabled function modules and are created in the Function Builder of the ABAP Workbench.
List of Standardized BAPIs:
- BAPIs for Reading Data - GetList() , GetDetail() , GetStatus() , ExistenceCheck()
- BAPIs for Creating or Changing Data- Create() ,Change(),Delete() and Undelete() ,
- BAPIs for Mass Processing -ChangeMultiple(), CreateMultiple(), DeleteMultiple().
How to create a BAPI
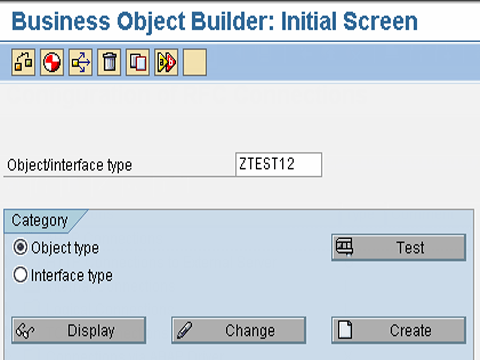
Step 1.Go to transaction swo1 (Tools->Business Framework -> BAPI Development ->Business Object builder ) .Select the business object, according to the functional requirement for which the BAPI is being created.
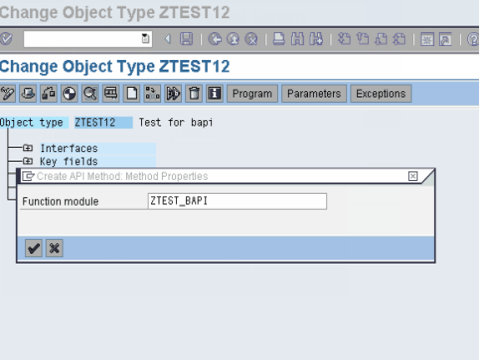
Step2.Open the business object in change mode. Then Select Utilities ->API Methods ->Add method.Then enter the name of the function module and select Continue.
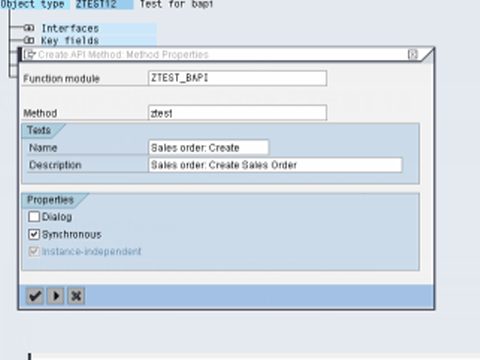
Step 3.In the next dialog box, following information needs to be specified :
- Method : Suggest an appropriate name for the method,
- Texts : Enter description for the BAPI,
- Radio buttons : Dialog, Synchronous, Instance-independent . BAPI 's are usually implemented synchronously.
Step4.To create the method select Yes in the next dialog box.
Step5.After the program has been generated and executed, check the program in the method just created.Thus , a BAPI is created.
Testing the BAPI
You can test the BAPI by Testing the individual method of the Business Object in the Business Object Builder. ( or one can use the transaction 'SWUD' to test the method ) .
Releasing and freezing the BAPI
- To release the BAPI , first release the function module ( using transaction se37 ) .
- Set the status of the method to 'released' in the Business Object Builder ( using transaction SWo1 - Edit-> change status-> released. )
You can also use the BAPI Explorer (Transaction code BAPI) for 360' view on BAPI
Q1. What is BAPI in SAP
Ans: BAPI is a Business Application Programming which provides access to processes and data in business application systems such as R/3. BAPIs are defined as API methods of SAP business object types. Business object types and their BAPIs are described and stored in the Business Object Repository (BOR). A BAPI is implemented as a function module, that is stored and described in the Function Builder.
Or
BAPIs are defined as API methods of SAP Business Object Types. These object types are used within the Business Framework to enable object-based communication between components. Business objects and their BAPIs enable object orientation to be used in central information processing in companies.
Q2. Explain the steps to create a BAPI?
Ans:
- 1.Creating a structure in SE11
- 2.Creating the function module in SE37
- 3.Creating the business object in SWO1
- 4.Viewing the created BAPI in BAPI Explorer
- 5.Test the BAPI.(BAPI tcode)
Q3. What are the uses of BAPI?
Ans: Using BAPI,we can connect :- New R/3 components.
- Non-SAP software.
- Legacy systems.
- Isolating components within the R/3 System .
- Connecting R/3 Systems to the Internet.
- PC programs.
- Workflow applications.
Q4. What is the difference between BAPI and RFC?
Ans:
BAPI:
BAPI is a RFC enabled function module and we create business objects and registered in the BOR (Business Object Repository) which can be accessed outside the SAP system by using other applications (Non-SAP) Languages such as VB or JAVA. That time we only define the business object and its methods from external system.
RFC:
Communication between applications of different systems in the SAP environment including connections between SAP systems as well as between SAP systems and non-SAP systems. Remote Function Call (RFC) is the standard SAP interface for communication between SAP systems. The RFC calls a function to be executed in a remote system.
Q5. What are the types of RFCs
Ans:
- Synchronous RFC
- Transactional RFC (tRFC)
- Queued RFC (qRFC)
Q6.What are RFC interfaces?
Ans: A calling interface for ABAP Programs
A calling interface for Non-SAP programs.
Q7. How do you call the RFC FM in the ABAP program?
Ans: CALL FUNCTION...DESTINATION statement. The DESTINATION parameter tells the SAP System that the called function runs in a system other than the callers.
Q8. What are the functions of RFC?
Ans:
- Converting all parameter data to the representation needed in the remote system
- Calling the communication routines needed to talk to the remote system.
- Handling communications errors, and notifying the caller, if desired ( using EXCEPTIONS parameter of the CALL FUNCTION).
- Convert the data into the format understandable by the remote (target) system.
- Call up certain routines which are necessary to start communication with the remote system.
- Handle errors that might occur in the process of communication.
- RFC can handle errors itself.
- every BAPI is a RFc whereas every RFC is not a BAPI.
- RFC's are not registered in the BOR.
Q9. What are the main characteristics of BAPI?
Ans:
- Support of synchronous and asynchronous communication.
- Support of machine-to-machine and human-to-machine communication.
- Communication support for components that are narrowly linked and coupled through the Internet.
Q10. What is the Business Objects type in SAP?
Ans: A business object type is the representation of a business object, like an human work force or a Invoice, in an SAP System. It encompasses both the functions and the data into single object.
Q11. What are the advantages of Business Objects type in SAP?
Ans: We can reduce the complexity of Systems structure by dividing the complex structures into smaller units.
Q12. What is the Business Object Repository?
Ans: The Business Object Repository (BOR) is root access point for the SAP business object types and their BAPIs. The BOR was developed for SAP Business Workflow.
Q13. What are the uses of Business Object Repository?
Ans:
- Allows an object-oriented view of all data and processes in an SAP System.
- Arranging the various business object types according to the component hierarchy.
- It ensures BAPI interface stability.
- It manages BAPIs in release updates.
- It creates instances of SAP business objects.
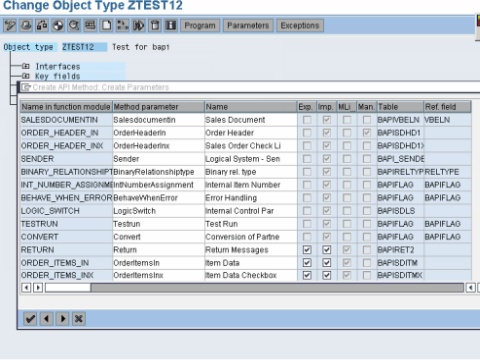
Q14. What is the Returning parameter in BAPI?
Ans:The return parameter RETURN contains success or error messages for the BAPI, and depending on the SAP R/3 Release has the dictionary structure BAPIRETURN, BAPIRETURN1, BAPIRET1, BAPIRET2.
Question 1. What Is Bapi In Sap?
Answer :
BAPI is a Business Application Programming which provides access to processes and data in business application systems such as R/3. BAPIs are defined as API methods of SAP business object types. Business object types and their BAPIs are described and stored in the Business Object Repository (BOR). A BAPI is implemented as a function module, that is stored and described in the Function Builder.
Question 2. Explain The Steps To Create A Bapi?
Answer :
- Creating a structure in SE11
- Creating the function module in SE37
- Creating the business object in SWO1
- Viewing the created BAPI in BAPI Explorer
- Test the BAPI.(BAPI tcode)
SAP ABAP Interview QuestionsQuestion 3. What Are The Uses Of Bapi?
Answer :
Using BAPI,we can connect :
- New R/3 components.
- Non-SAP software.
- Legacy systems.
- Isolating components within the R/3 System .
- Connecting R/3 Systems to the Internet.
- PC programs.
- Workflow applications.
Question 4. What Is The Difference Between Bapi And Rfc?
Answer :
BAPI:
BAPI is a RFC enabled function module and we create business objects and registered in the BOR (Business Object Repository) which can be accessed outside the SAP system by using other applications (Non-SAP) Languages such as VB or JAVA. That time we only define the business object and its methods from external system.
RFC:
Communication between applications of different systems in the SAP environment including connections between SAP systems as well as between SAP systems and non-SAP systems. Remote Function Call (RFC) is the standard SAP interface for communication between SAP systems. The RFC calls a function to be executed in a remote system.
SAP ABAP TutorialQuestion 5. What Are The Types Of Rfcs?
Answer :
- Synchronous RFC
- Transactional RFC (tRFC)
- Queued RFC (qRFC)
SAP ABAP Web Dynpro Interview QuestionsQuestion 6. What Are Rfc Interfaces?
Answer :
- A calling interface for ABAP Programs
- A calling interface for Non-SAP programs.
Question 7. How Do You Call The Rfc Fm In The Abap Program?
Answer :
CALL FUNCTION...DESTINATION statement. The DESTINATION parameter tells the SAP System that the called function runs in a system other than the callers.
SAP ABAP Web Dynpro Tutorial SAP BODS Interview QuestionsQuestion 8. What Are The Functions Of Rfc?
Answer :
- Converting all parameter data to the representation needed in the remote system
- Calling the communication routines needed to talk to the remote system.
- Handling communications errors, and notifying the caller, if desired ( using EXCEPTIONS parameter of the CALL FUNCTION).
- Convert the data into the format understandable by the remote (target) system.
- Call up certain routines which are necessary to start communication with the remote system.
- Handle errors that might occur in the process of communication.
- RFC can handle errors itself.
- every BAPI is a RFc whereas every RFC is not a BAPI.
- RFC's are not registered in the BOR.
Question 9. What Are The Main Characteristics Of Bapi?
Answer :
- Support of synchronous and asynchronous communication.
- Support of machine-to-machine and human-to-machine communication.
- Communication support for components that are narrowly linked and coupled through the Internet.
SAP ALE Interview QuestionsQuestion 10. What Is The Business Objects Type In Sap?
Answer :
A business object type is the representation of a business object, like an human work force or a Invoice, in an SAP System. It encompasses both the functions and the data into single object.
SAP BODS TutorialQuestion 11. What Are The Advantages Of Business Objects Type In Sap?
Answer :
We can reduce the complexity of Systems structure by dividing the complex structures into smaller units.
SAP BDC Interview QuestionsQuestion 12. What Is The Business Object Repository?
Answer :
The Business Object Repository (BOR) is root access point for the SAP business object types and their BAPIs. The BOR was developed for SAP Business Workflow.
SAP ABAP Interview QuestionsQuestion 13. What Are The Uses Of Business Object Repository?
Answer :
- Allows an object-oriented view of all data and processes in an SAP System.
- Arranging the various business object types according to the component hierarchy.
- It ensures BAPI interface stability.
- It manages BAPIs in release updates.
- It creates instances of SAP business objects.
SAP Smart Forms TutorialQuestion 14. What Is The Returning Parameter In Bapi?
Answer :
The return parameter RETURN contains success or error messages for the BAPI, and depending on the SAP R/3 Release has the dictionary structure BAPIRETURN, BAPIRETURN1, BAPIRET1, BAPIRET2.
Question 15. What Are The Basic Components Of Sap R/3 Business Framework ?
Answer :
- Business Components:SAP Business Components provide autonomous business functions and consist of business objects. For example, the business objects Employee and Applicant are assigned to the Business Component Human Resources. Business processes are either implemented within a Business Component or across several Components (distributed business processes).
- Business Objects:The object-oriented structure of the R/3 System is based on Business Objects. They encapsulate business data and functionality and define the functional scope and boundaries of a Business Component.
- Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPI):BAPIs are interfaces for Business Objects. Together with the Business Objects, BAPIs define and document the interface standard at the business level.
- Integration Service, Application Link Enabling (ALE):The ALE Integration Service enables the integration of business processes that are carried out in different R/3 and non-SAP systems. This service is based on the system-wide distribution of Business Objects using the ALE distribution model.
- Communication Services:These are the communication technologies, for example, Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) and Remote Function Call (RFC) that use the Business Framework to access BAPIs.
SAP Smart Forms Interview QuestionsQuestion 16. What Is Sap Business Objects ?
Answer :
- A business object type, which represents of a business entity in the SAP R/3 System, encompasses both the functionality (in the form of methods) and the data (in the form of attributes) of this entity. The implementation details of the business object type are hidden from the user. The business object type is accessed through defined functions (methods). This is referred to as encapsulation.
- Business object types form the point of entry to the data and the functionality of the SAP R/3 System. At the business object type level, both non-SAP systems and the various SAP business components can communicate with each other.
- The business object type Sales Order represents a customer’s request to the company to supply a particular quantity of material at a certain point in time or to perform services at a certain point in time. A specific sales order is identified by a sales document number. The business object type contains all the necessary information for a sales order: sold-to party, sales organization, document date, net value of the order, and currency of the sales and distribution document.
Answer :
BAPIs are defined as API methods of SAP Business Object Types. These object types are used within the Business Framework to enable object-based communication between components. Business objects and their BAPIs enable object orientation to be used in central information processing in companies.
SAP ABAP Enhancement Interview QuestionsQuestion 18. What Need To Be Taken Care While Handling Database Transaction In Bapi ?
Answer :
- A transaction is completed either using a COMMIT WORK command or a ROLLBACK command. A BAPI transaction must be ended by calling the BAPIs BapiService.TransactionCommit() or BapiService.TransactionRollback().
- The call of a BAPI must not trigger further LUWs that are independent of the BAPI.
For this reason BAPIs must not contain the following commands:
- CALL TRANSACTION
- SUBMIT REPORT
- SUBMIT REPORT AND RETURN
SAP ABAP Web Dynpro Interview QuestionsQuestion 19. What Is Bor (business Object Repository) ?
Answer :
- The Business Object Repository (BOR) is the central access point for the SAP business object types and their BAPIs. The BOR contains all the relevant information on the SAP business object types, their key fields, and their BAPI methods that are needed to integrate the correct object type definitions and BAPI calls in an application program. This makes the integration of middleware (such as the DCOM Connector, ActiveX Controls, CORBA Gateway, and so on) possible.
- Creates instances of SAP business objects. The runtime environment of the BOR receives requests to create runtime objects from client applications and creates the appropriate object instances.
Question 20. What Is The Difference Between Rfc And Bapi?
Answer :
BAPI :
- BAPI is a library of function modules released by SAP to the public so that they can interface with SAP.
- There is a Business Object Associated with a BAPI. So a BAPI has an Interface, Key Field, Attributes, Methods, and Events.
- Outside world (JAVA, VB, .Net or any Non SAP system) can connect to SAP using a BAPI.
- Error or Success messages are returned in a RETURN table.
RFC:
- RFC is nothing but a remote enabled function module. So if there is a Function Module in SAP system 1 on server X , it can be called from a SAP system 2 residing on server Y.
- No Business Object is associated with a RFC.
- Non–SAP world cannot connect to SAP using RFC.
- RFC does not have a return table.
SAP ABAP Report Developer Interview QuestionsQuestion 21. What Is The Difference Between Bdc And Bapi?
Answer :
BAPI:
- BAPI is faster than BDC.
- BAPI directly updates database.
- BAPI would generally used for small data uploads.
- For processing errors, the Return Parameters for BAPI should be used.This parameter returns exception messages or success messages to the calling program.
BDC:
- BDC goes through all the screens as a normal user would do and hence it is slower.
- Background and Foreground processing options are available for BDC.
- BDCs would be preferred for large volumes of data upload since background processing option is available.
- Errors can be processed in SM35 for session method and in the batch input program for Call Transaction method.
Question 22. What Are The Steps For Creating A Bapi ?
Answer :
Stage1: Creating a structure in SE11
Stage2: Creating the function module in SE37
Stage 3: Creating the business object in SWO1
Stage 4: Viewing the created BAPI in BAPI Explorer
What is BAPI in SAP?
Explain the steps to create a BAPI?
What are the uses of BAPI?
What is the difference between BAPI and RFC?
What are the types of RFCs
What are RFC interfaces?
How do you call the RFC FM in the ABAP program?
What are the functions of RFC?
What are the main characteristics of BAPI?
What is the Business Objects type in SAP?
What are the advantages of Business Objects type in SAP?
What is the Business Object Repository?
What are the uses of the Business Object Repository?
What is the Returning parameter in BAPI?
- Business Components
SAP Business Components provide autonomous business functions
and consist of business objects. For example, the business objects Employee and Applicant are assigned to the Business Component Human Resources. Business processes are either implemented within a Business Component or across several Components (distributed business processes). - Business Objects
The object-oriented structure of the R/3 System is based on Business Objects. They encapsulate business data and functionality and define the functional scope and boundaries of a Business Component. - Business Application Programming Interfaces (BAPI)
BAPIs are interfaces for Business Objects. Together with the Business Objects, BAPIs define and document the interface standard at the business level. - Integration Service, Application Link Enabling (ALE)
The ALE Integration Service enables the integration of business processes that are carried out in different R/3 and non-SAP systems. This service is based on the system-wide distribution of Business Objects using the ALE distribution model. - Communication Services
These are the communication technologies, for example, Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) and Remote Function Call (RFC) that use the Business Framework to access BAPIs.
- A business object type, which represents of a business entity in the SAP R/3 System, encompasses both the functionality (in the form of methods) and the data (in the form of attributes) of this entity. The implementation details of the business object type are hidden from the user. The business object type is accessed through defined functions (methods). This is referred to as encapsulation.
- Business object types form the point of entry to the data and the functionality of the SAP R/3 System. At the business object type level, both non-SAP systems and the various SAP business components can communicate with each other.
- The business object type Sales Order represents a customer’s request to the company to supply a particular quantity of material at a certain point in time or to perform services at a certain point in time. A specific sales order is identified by a sales document number. The business object type contains all the necessary information for a sales order: sold-to party, sales organization, document date, net value of the order, and currency of the sales and distribution document.
BAPIs are defined as API methods of SAP Business Object Types. These object types are used within the Business Framework to enable object-based communication between components. Business objects and their BAPIs enable object orientation to be used in central information processing in companies.
- A transaction is completed either using a COMMIT WORK command or a ROLLBACK command. A BAPI transaction must be ended by calling the BAPIs BapiService.TransactionCommit() or BapiService.TransactionRollback().
- The call of a BAPI must not trigger further LUWs that are independent of the BAPI. For this reason BAPIs must not contain the following commands:
CALL TRANSACTION
SUBMIT REPORT
SUBMIT REPORT AND RETURN
- The Business Object Repository (BOR) is the central access point for the SAP business object types and their BAPIs. The BOR contains all the relevant information on the SAP business object types, their key fields, and their BAPI methods that are needed to integrate the correct object type definitions and BAPI calls in an application program. This makes the integration of middleware (such as the DCOM Connector, ActiveX Controls, CORBA Gateway, and so on) possible.
- Creates instances of SAP business objects. The runtime environment of the BOR receives requests to create runtime objects from client applications and creates the appropriate object instances.
- BAPI :
- BAPI is a library of function modules released by SAP to the public so that they can interface with SAP.
- There is a Business Object Associated with a BAPI. So a BAPI has an Interface, Key Field, Attributes, Methods, and Events.
- Outside world (JAVA, VB, .Net or any Non SAP system) can connect to SAP using a BAPI.
- Error or Success messages are returned in a RETURN table.
- RFC
- RFC is nothing but a remote enabled function module. So if there is a Function Module in SAP system 1 on server X , it can be called from a SAP system 2 residing on server Y.
- No Business Object is associated with a RFC.
- Non–SAP world cannot connect to SAP using RFC.
- RFC does not have a return table.
- BAPI
- BAPI is faster than BDC.
- BAPI directly updates database.
- BAPI would generally used for small data uploads.
- For processing errors, the Return Parameters for BAPI should be used.This parameter returns exception messages or success messages to the calling program.
- BDC
- BDC goes through all the screens as a normal user would do and hence it is slower.
- Background and Foreground processing options are available for BDC.
- BDCs would be preferred for large volumes of data upload since background processing option is available.
- Errors can be processed in SM35 for session method and in the batch input program for Call Transaction method.
- Stage1: Creating a structure in SE11
- Stage2: Creating the function module in SE37
- Stage 3: Creating the business object in SWO1
- Stage 4: Viewing the created BAPI in BAPI Explorer
RFC Vs BAPI
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment