AMDP SAP HANA
AMDP
After reading this blog reader would have a clear idea why SAP recommends CDS views, what is AMDP and what are the benefits of CDS and AMDP over other methods.
As we all know HANA works on Push down techniques means, to make HANA DB do the calculations which was earlier done by application layer in ECC.
Further, Push down technique can be achieved using two approaches:
- Bottom-Up approach
- Top-Down approach

1. Bottom-Up approach :
Here In Bottom-Up, we create views (Calculation view, Attribute view, Analytic view) at HANA DB layer with HANA Modelling and these views are later exposed and used in ABAP layer via external views.
External Views :
- Read only
- Monitored by ABAP dictionary
- Can be used in ABAP programs to access data available in the form of Information Views in SAP HANA DB.
- More optimized than stored procedures. (discussed below)
Summing up..
- Create HANA view in DB layer
- Create external view
- Use external view in application
So, this is how we use Bottom-Up approach.
Note: Before ABAP 7.4 we were using external view approach.
Question?? Why SAP recommends Top-Down approach
2. Top-Down approach :
In Top-Down, we create objects using ABAP code that can leverage power of SAP HANA. Here comes CDS and AMDP into picture.
What are we doing in Top-Down?…We are creating models in application layer and it is going to create same in DB layer. Its like, we are using door of application layer to create objects/models in HANA DB.
Drawbacks of Bottom-Up approach :
- Need additional license to create views in DB layer (For ABAP and HANA db both)
- Dual maintenance
- Synchronization of changes (If any change made in DB layer (models) it should be reflected in App. layer)
- Transport Management (need separate transports to move across ABAP and HANA db if any changes made in both)
- Additional license cost (maintaining both HANA and ABAP layer)
This answers to the question why SAP recommends Top-Down approach.
As we know now Top-Down has benefit over Bottom-Up. So, whatever we were achieving via Bottom-Up we will be achieving same by Top-Down.
In Bottom-Up, we were creating views and later using them in our application layer by exposing them i.e. creating external view. Now, in Top-Down, we achieve this via CDS. We create CDS views in ABAP layer and as we activate or execute the same 2 views created.
- ABAP View (at DDIC layer), also called DDL SQL view
- HANA View (at HANA DB layer)
Other part was Procedures, we were writing procedures in Bottom-Up approach, directly in HANA DB using native SQL query. Procedures are written if the business requirement is complex and same can’t be achieved via information views.
For exposing Procedures, we can’t use external views so for that we were using stored procedure proxy.
Bottom line :
- For views in Bottom-Up, replacement in Top-Down was CDS
- For Procedures in Bottom-up, replacement in Top-Down is AMDP
CDS (Core Data Services) :
- Defined in ABAP repository using SQL DDL syntax
- use open SQL language
- CDS is executed as a single statement, hence we can’t put a debugger inside.
AMDP (ABAP Managed Database Procedures) :
- Simple ABAP class method containing DB specific procedure coding.
- use native SQL language
- Activate AMDP debugger :: Terminate AMDP debugger
- The code within the method is pushed to the DB layer and executed within the DB
- Should be used only if DB specific functions that do not exist in open SQL needed to be accessed.
CDS VS AMDP :
- In AMDP, we can call one function inside the other, it is helpful in returning multiple result set on complex logics. Whereas, CDS is dedicated for single set of logic and return only one result set.
- CDS views can be created to read and process data at DB layer. Whereas AMDP can be created to process and modify data at DB layer.
- AMDP is used to work with stored procedures, which further go to HANA DB layer and execute that. This functionality can’t be achieved by Open SQL and CDS.
Common features/ Benefits of CDS and AMDP :
- We are creating/using DB Procedures in AMDP and views in CDS without having access of HANA DB layer.
- AMDP and CDS can be created in eclipse only not in GUI as ADT (ABAP Development Tool) plug-in is needed for this (also in HANA Studio).
- CDS and AMDP does not need HANA license, when it is executed first time, it automatically create views and procedures respectively in HANA DB. Next time it will take same from HANA DB buffer.
- Transferring data to other systems, CDS will create views and AMDP will create procedures automatically in the new system.

Note: CDS Views are compatible with any database whereas AMDP needs HANA as a database and this is the reason CDS is more popular and is in demand.
1. What is ABAP Managed Database Procedure?
ABAP Managed Database Procedure (AMDP) is a class-based framework for managing and calling database procedures (or) stored procedures in ABAP.
2. What is an AMDP Class?
A global class which contains marker tag interface IF_AMDP_MARKER_XXX, where XXX means database like IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB for SAP HANA database.
Also Read: Introduction to ABAP Managed Database Procedure.
3. What is the transaction code to check the missing authorizations for AMDP execution?
SICK
4. Can we create/edit AMDP in SAP GUI using transaction SE24?
No, ABAP Managed Database Procedures (AMDP) are created and managed using Eclipse-based ABAP Development Tools(ADT).
5. How to check if database support AMDP procedures?
We can the database support by using the constant CALL_AMDP_METHOD of the class CL_ABAP_DBFEATURES.
6. Which one you choose AMDP or Open SQL? If the task can be achieved by both.
If the task can be achieved by both it is recommended to use Open SQL or ABAP CDS.
7. How many types of AMDP methods exists?
There are two types AMDP methods,
- AMDP Procedures which are implemented with addition BY_DATABASE_PROCEDURE and
- AMDP Function which is implements with addition BY_DATABASE_FUNCTION
8. Can a constructor in the class implemented as AMDP method?
No, Constructors cannot be implemented as AMDP methods.
9. How to call ABAP procedure in an ABAP program?
An AMDP procedure implementation method is called from an ABAP program in the same as normal SE24 ABAP class method calling.
10. If your database does not support AMDP what are the alternatives?
In database system which does not support AMDP, we can use Open SQL or Native SQL to implement the same functionality.
11. Does AMDPs support automatic client handling?
No, AMDP does not support automatic client handling, when accessing database tables in AMDP method client ID must be specified explicitly.
12. Can we implement exception handling for AMDP procedure methods?
Yes, exception handling is supported for AMDP procedure methods. Some of the exceptions are
- CX_AMDP_VERSION_MISMATCH
- CX_AMDP_DBPROC_CREATE_FAILED
- CX_AMDP_NATIVE_DBCALL_FAILED
- CX_AMDP_NATIVE_DBCALL_FAILED
- CX_AMDP_RESULT_TABLE_ERROR
13. Does AMDP function implementations support exception handling?
No exceptions can be declared for AMDP function implementations.
14. Can we enhance AMDP standard methods?
No, AMDP method does not support implicit enhancement options.
15. Can we use COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements in an AMDP method?
No, COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements are not permitted.
16. How can we return data from AMDP method?
We can return data from AMDP method using CHANGING parameters.
17. Are CHANGING parameters are pass by value (or) pass by reference?
The parameters must be declared using VALUE for pass by value. Pass by reference is not permitted.
18. Can we return data from AMDP method using RETURNING parameters?
No, return values can not be declared as RETURNING
19. Is it possible to identify an AMDP method by declaration section of the method?
An AMDP method cannot be identified as an AMDP method in the declaration section of the class but only in the implementation section.
20. Can AMDP method be declared as static method in the AMDP class?
Yes AMDP methods is declared in an AMDP class like a regular static method (or) instance method.
21. Can AMDP class contains regular methods?
An AMDP class can contain both regular methods and AMDP methods.
What is an AMDP procedure?
ABAP Managed Database Procedures are a framework for managing and calling stored procedures or database procedures in AS ABAP. An ABAP Managed Database Procedure (or AMDP procedure) is a procedure written in a database-specific language ( Native SQL, SQL Script, L, …) implemented in an AMDP method of an AMDP class.
What are different approaches to create an AMDP procedure?
| Bottom-Up Approach AMDP | Top-Down approach AMDP |
| From ABAP 7.40 version , We can call the stored procedure by using AMDP proxies. | Database procedure coding will be included in the ABAP coding itself. |
| Call of the procedure proxy in ABAP triggers the procedure execution in SAP HANA | Creates the databse procure at the time of first call of the method. |
| DISADV: dabase development and ABAP developments are managed by different life cycle management Database procedure proxies are still recommended when using a secondary database connection to access SQL Script procedures that exist in a different SAP HANA database. | Single transport container is suffient. No need of hana delivery unit and hana transport container. |
What is the procedure to create AMDP procedure from normal ABP class?



what are the restrictions for AMDP class compared to normal ABAP class creation?
An AMDP is declared in an AMDP class like a regular static method or instance method in any visibility section. An AMDP method cannot be identified as an AMDP method in the declaration section of the class.
The following restrictions apply, however, with respect to the parameter interface:
- The typing of the parameters cannot be generic. Only elementary data types and table types with a structured row type can be used. The row type of a tabular type can only contain elementary data types as components
- A parameter cannot be typed with a data type that references one of the obsolete predefined data types DF16_SCL or DF34_SCL in ABAP Dictionary.
- The parameters must be declared using VALUE for pass by value. Pass by reference is not permitted.
- Return values cannot be declared using RETURNING.
- Only input parameters can be flagged as optional and every optional parameter must have a replacement parameter declared using DEFAULT. Only literals or constants can be specified as replacement parameters.
- Parameter names:
- Parameter names cannot start with the characters “%_”.
- The parameter name connection can only be used for an input parameter of type DBCON_NAME, if the name of the database connection can be passed to the input parameter.
- The parameter name client is reserved for future enhancements.
- The parameter name endmethod is not permitted.
- With RAISING the exception classed listed under AMDP – exception classes can be specified to handle these classes for a call. Other exceptions cannot be handled. No non-class-based exceptions can be created using the addition EXCEPTIONS.
The following restrictions apply to method implementation:
- DDL statements are not permitted for creating, changing or deleting database objects.
- Local temporary database objects cannot be accessed.
- Database commits and rollbacks cannot be executed. The statements COMMIT and ROLLBACK in particular are not permitted. LUWs should always be handled in the ABAP program, to ensure data consistency between procedures.
- Write access to database tables, for which SAP buffering is activated, is not permitted.
- AMDP methods do not have any implicit enhancement options.
In calculation view we cannot apply filtering in default projection node.
In calculation view in join node we cannot do referential join.
In join node we cannot do filtering.
we could join without projection but we cannot do filtering.
In star join we can use referential join.
which interface do we need to include in AMDP class?
IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB.
what are AMDP BADI’s and what are its restrictions in using it compared to normal badi’s ?
In addition to the option of implementing BAdI methods of a normal BAdI as AMDP methods and making these methods callable by using CALL BADI, it is also possible to create special AMDP BAdIs. A AMDP BAdI is a BAdI, which is labeled accordingly in BAdI Builder and has the following properties:
- Definition and implementation
- An AMDP BAdI does not currently have any filters.
- Fallback BAdI implementation classes must be specified.
- Every BAdI method of an AMDP BAdI must be an AMDP method.
- Every AMDP method must be implemented for the same database system.
- Call BAdI methods
- The AMDP methods of an AMDP BAdI can be called like normal BAdl methods with GET BADI and CALL BADI.
- The AMDP procedures created on the database of an AMDP BAdI can be called here (like all AMDP procedures) from other AMDP methods in the same database system. These AMDP procedures are specified using the name of a BAdI implementation class. The usage must be declared after the addition USING of the calling method.
Use of Secondary Database Connection when calling AMDP Methods
class zcl_demo_amdp definition public final create public .
public section.
interfaces if_amdp_marker_hdb .
methods increase_price importing
value(connection) type dbcon_name default ”
value(clnt) type sy-mandt
value(inc) type sflight-price
raising cx_amdp_error.
endclass.
**** Call using named Database Connection “SECDB”
lo_amdp_demo->increase_price(
exporting connection = ‘R/3*SECDB’
clnt = ‘000’
inc = 10 ).
what is the difference between AMDP procedure and CDS view?
Can we create hana modelling on row stored table?
No, Because hana modeler only supports column stores. For row store we cannot create hana modelling.
What are the different types of hana modelling views?
- Attribute view
- Analytic view
- Calculation view
What is the difference between row stored table and column stored table?
Adva: Data compression, faster read and write access, flexibility and parallel processing, perform aggregations and calculations at higher speed.
While runnign a simple select query, full row has to be printed in output so it is advisable to store table as Row based in this scenario.
What is an attribute view?
3 types of attribute views. Standard , time, derived
scenario and details blocks
in analytical view we will have a star schema, data foundation and semantics.
In analytical view we can take only one table as central entity and measures can be taken from that table only.
We should specify the table for central entity in data foundation property of the analytical view.
we cannot create hierarchies in analytical views but we can use the hieraarchies of the attribute views.
Main points:
- Use field lists instead of SELECT *.
- Use joins where possible . ( instead of nested selects or select , for all entries).
- familiarize yourself with advanced SQL features and how to work with SQL script which you might need when implementing calculation views / stored procedures in SAP HANA later
- think about whether your application in the future will only support SAP HANA or all databases
- Make use of ABAP test cockpit on SAP HANA.
- WPA: workflow and posting assistant
what is DSO activation queue in the case of direct extractor connection ?
MDX is used for EXCEL reporting.
BICS: business intellligence consumer services/
sap business object design studio(ZEN)
Database Procedure as a function stored and executed in the database.(lower level data processing logic)
MDX : multi dimension expression engine
Different database procedures:
Pre-update procedure – this procedure does not return any data, it only performs an operation on one or more databases. All pre-update procedures in an information link will always be executed before any query procedure.
Query procedure – just like a database table, this procedure returns data.
Post-update procedure – this procedure does not return any data, it only performs an operation on one or more databases. All post-update procedures in an information link will always be executed after any query procedure.
- SAP HANA architecture:
 A running SAP HANA system consists of multiple communication processes(services).
A running SAP HANA system consists of multiple communication processes(services).- Well defined database interfaces( ODBC ,JDBC) to communicate with the database management system functioning as a data source.
- The main SAP HANA database management component is known as the index server. Which contains the actual data stores and engines for processing the data. The index server processes incoming SQL and MDX statements
- SQL Script programming avoids the unnecessary loading of data into application server.
- In addition to SQL script: SAP HANA supports a framework for the installation of specialized and optimized functional libraries. Which are tightly integrated with different data engines of the index server. Two of these functional libraries are the SAP HANA Business Functional Library (BFL) and the SAP HANA Predictive Analytics Library(PAL)
- BFL and PAL functions can be called directly from within SQL Script.
- The database persistence layer is responsible for durability and atomicity of transactions.
- The index server uses the preprocessor server for analyzing text data and extracting the information on which the text search capabilities are based.
- In a distributed system , the name server knows where the components are running which data is located on which server.
- SAP HANA Extended Application Services:
In extended application services we can use MVC architecture.

You can effectively eliminate the overhead of the middle-tier between the user interface and the data-intensive control logic.

By using Extended Application Services Provides a comprehensive set of embedded services that provide end-to-end support for web-based applications.
No data is stored in the SAP HANA XS server itself.
- How to handle client dependency in CDS views?
taken into account, when you access client dependent data sources with Open SQL.
What are client dependent data sources?
- A database table or classic view defined in the ABAP Dictionary is client dependent if the first column is a client column with the built-in dictionary type CLNT.
- The client dependency and client handling of CDS entities (CDS views and CDS table functions) is defined by annotations. With release 7.51 a new annotation @CLientHandling is introduced for that. The previous annotation @ClientDependent becomes obsolete.
CDS Views
For CDS views you use the annotation @CLientHandling in order to define the client dependency and how client handling is done internally. For that you can specify the following two sub annotations:
@ClientHandling.type: #INHERITED | #CLIENT_DEPENDENT | #CLIENT_INDEPENDENT
How to find whether the program runs on hana or not?
First of all, we would need to make sure that the custom ABAP programs can work on HANA DB. It is not the compilation errors, but rather errors from the functionality perspective. For this purpose, SAP has provided this variants in Code inspector (SCI). We should take all the custom objects, and run these two checks.
- FUNCTIONAL_DB
- FUNCTIONAL_DB_ADDITION
How to identify whether the database is hana or not?
is_in_memory_db = abap_true.
WRITE: ‘HANA DB’.
ENDIF.
What is the difference between Attribute View and CDS view?
An attribute view is one of the view types available in the HANA modelling environment.
Attribute view is intended to join tables together.
One scenario might be to use an attribute view as a single dimension in analytical view.
CDS View : CDS is a layer above the “Pure” database in order to define semantically-enriched data models. In contrast to the attribute view a CDS document can define tables, Views, table types, associations and annotations.
You can use CDS is much more powerful than a plain attribute view.
Attribute views are one simple type of views intended to join tables. The attribute views are HANA managed, So in order to address them in ABAP you would need an external view.
Transportation is also an issue as the life cycle of the attribute view is managed by HANA whereas the external view is managed by ABAP.
Definition of ABAP Managed Database Procedure (AMDP)
ABAP Managed Database Procedure (AMDP) is a class-based framework for managing and calling database procedure in ABAP.
Bottom-Up Approach with Database Procedure Proxies
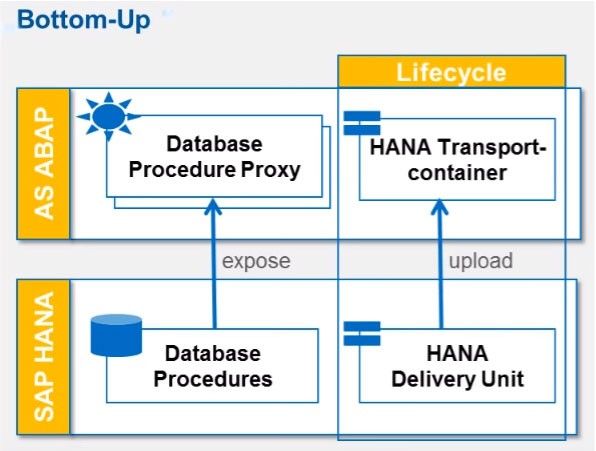
As we know the currently, the optimized way for using HANA procedures in ABAP is provide by Database Procedure Proxies which was introduced with Application ABAP 7.4 with service package 2.
In this Bottom-up approach, the database has first to be developed in HANA server and then expose the Database Procedure Proxy in ABAP server. To ensure that dependent ABAP and HANA content is exported together in HANA Transport Container and HANA Delivery Unit are required.
This Bottom-UP approach involves the problem of having a different independent life cycle in TMS (Transport Management System) for the HANA and ABAP content.
ABAP Managed Database Procedure (AMDP) (Top-Down Approach)
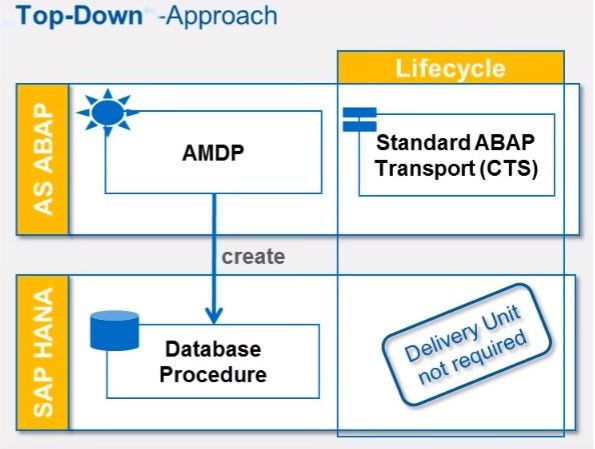
The solution for the problem faced in Bottom-Up approach is provided by ABAP Managed Database Procedure (AMDP).
This Top-Down approach enables developers to create a managed whole life-cycle of HANA procedure in ABAP Development Environment.The AMDP is implemented as a method of a global class which is marked with specific interfaces called as AMDP class.
In corresponding to AMDP class, the HANA based SQL class is created at the first call of the method.
Advantage of AMDP Process
- The main advantage of this method that only the AMDP class has to be transported wit ABAP transport mechanism.
- No HANA delivery or HANA transport system is required in this process.
- Developers only need ABAP development tools for building and managing the CDS view. There is no need for additional HANA development tools.
Example of AMDP Class Definition
CLASS CL_AMBP_EXAMPLE DEFINITION.
PUBLIC SECTION.
INTERFACES IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB. //Marker Interface for HANA DB//
METHODS process //Only ABAP code is possible//
IMPORTING it_param TYPE type1
EXPORTING et_param TYPE type2.
METHODS execute //SQLScript or ABAP code both are possible//
IMPORTING VALUE(it_param) TYPE type1
EXPORTING VALUE(et_param) TYPE type2. //specific parameter interface required//
CHANGING VALUE(ch_param) TYPE type3
ENDCLASS.
AMDP Class Implementation
CLASS CL_AMDP_EXAMPLE IMPLEMENTATION
METHODS process
// Write ABAP source code here//
...
ENDMETHOD
METHOD execute BY DATABASE PROCEDURE //AMDP method marker//
FOR HDB //Database platform//
LANGUAGE SQLScript //Database language//
[OPTIONS READ-ONLY] //Database-specific options//
USING name1 name2 etc... //List of used DDIC entities and AMDPs//
//Write here the SQLScript coding//
select * from dummy;
...
ENDMETHOD.
ENDCLASS.
Features of ABAP Managed Database Procedure (AMDP)
- Static check code and Syntax colouring are provided for embedded SQLScript
- The user can set a Background colour for better visibility AMDP methods in the class.
- The User can access other AMDP methods, ABAP dictionary view and ABAP tables in AMDP method.
- AMDP method are called like other regular ABAP methods.
- User can perform detailed analysis of various error during runtime in transaction ST22
- Modification or Enhancement of regular ABAP classes can be done by Users.
Q1. What is SAP HANA?
Ans. HANA is defined as High Performance Analytical Appliance, a full transactional RDBMS system given by SAP consisting of IMCE ( In-Memory Computing Engine ) which combine row based and column based architecture. It is capable of doing both OLTP and OLAP in a single box which includes both Hardware and Software Innovations. It is also knows as Hybrid Database System.
Hardware innovation
Reduction in memory and Chip (CPU) price
Multi core Processors
Operating systems are now available with high bit size 64 bit
8084 16 bit Address Bus
2n - 2
Software Innovation
Column Store v/s Row Store
Table Partitioning
High Compression of data
Parallel Processing
Q2. What is the difference between Row Storage and Column Storage?
Q3. What is a Schema in SAP HANA?
Ans. A Schema is a dedicated area of database which can be used to store database objects like table, packages, folders, procedures.
It provides a namespace for systems which connects to Database.
Q4. What are the improvements in NW 7.5 to leverage the strength of HANA?
Code to Data paradigm ( code-pushdown )
Massive Parallel Processing
Data Encoding
Columnar Store
Run Complex Algorithms
Transparent Optimization ( order in which select query will be written and executed which is done by DB abstraction layer – converts OPEN SQL from ABAP to Native SQL which is understood by DB )
Q5. Benefits of SAP NW 7.5?
Ans.
Transparent Optimization
SELECT QUERY : NetWeaver creates a query plan : Plan based Optimizer & Cost Based Optimizer , which decides the order/sequence in which query will be processed.
Allows more complex joins
Open SQL Enhancement
Extended the static code check and SQL performance analysis
Fast Data Access, Optimized data access
Reuse Components, ALV ,Fuzzy Search
Extension to open SQL
Features specific to HANA related artifacts
Standard programming guidelines by SAP
ABAP/ Fiori Applications
Q6. Points to be considered when Migrating to HANA?
Native SQL statements will not work – it will result into Runtime error - Dumps
EXEC SQL.
-Native Queries
SELECT ROWNUM, MATNR FROM SAPECC6.MARA;
ENDSQL.
If you have some indication to Database – not showstopper.
Db hits: ‘%_HINTS MSSQLNT ‘&prefer_join&’
Select orderid from table where amount < 300.
If you are doing a search based on non-pk columns in data based and you have not used ORDER BY clause in SQL statement, it can produce problems.
Direct access to database cluster/pool tables
Code Inspector: SCI – Quality checks of our code
When you release a transport from your dev. System a code inspector check is executed automatically.
Prio 1, 2, 3
Also Read: SAP HANA from Space Level
Q7. What are the Guidelines to be followed for SQL performance on ABAP on HANA?
Q8. What are different categories of Database Statements?
Ans. Database statements categories:
DDL – Data Definition language – Mainly used to create/change/delete new database objects.
SE11 – Data Dictionary which automatically produces the DDL statements for you.
CREATE, ALTER, DROP…
DML – Data Manipulation Language – statements which are used to manipulate data.
INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, MODIFY
DQL – Data Query Language – SELECT statement, GET
TCL – Transaction Control Statements (ACID) - COMMIT, Rollback
DCL – DATA Control Language – Security and access of data
GRANT, REVOKE ….
Q9. What is Normalization in ABAP on HANA?
Ans. Normalization concept means to reduce the redundancy of data.
Q10. What is ABAP Test Cockpit in ABAP on HANA?
Ans. Code inspector/ATC checks are static code findings against guidelines. These findings won’t help you to prioritize your list of improvements. You need real-time performance data to find which is the first program to fix.
Q11. How to do performance testing in PRD system? What are pre-requisites?
Ans. With SAP Netweaver 7.5 SP05 you can do performance trace in PRD system without much overhead, in two steps: 1st: Administor the SQLM ( tcode) – start and stop the trace. 2nd: Data: SQLMD ( tcode ) in the order of the potentially expensive statement.
In order to find performance trace priority list : use tcode : SWLT ( SQL Performance tuning worklist )
Q12. Class to calculate runtime in ABAP on HANA?
Ans: CL_ABAP_RUNTIME
Q13. How to specify client field in Native Query?
Ans: Using SELECT DISTINCT / CLIENT SPECIFIED / USING CLIENT
Q14. Tcode for EPM scenario?
Ans: SEPM_DG – Data Generator
Q15. What are different Code-pushdown techniques?
Ans:
SQL Queries _ imperative and declarative logic (use literals, arithmetic, logical expression inside the queries and using expressions like CEIL, FLOOR, ABS, TRUNC, FRAC can be part of Open SQL statements ),
CDS Views,
AMDP : ABAP Managed Data Procedures,
Information Models and consuming those in ABAP using proxy object techniques
Q16. What are Entry points?
Ans: Different ways in which an SQL query is getting called are called Entry points. Eg. Program, Background job, Function Module .. etc
Q17. What does NW 7.4 SP 05/NW 7.5 SP 02 offers in ABAP?
Ans: Enhancements in ABAP and OPEN SQL:
Provides Database Abstraction: - can connect to any db, where the database abstraction layer converts the OPEN SQL statements into Native SQL
Improvements in OPEN SQL Enhancements:
Escaping of HOST Variables: eg- “:” colon , “@”
Comma separated select list: SELECT col1, col2, col3 … , you have to use escape symbol for host variable
Right outer join available
Possible to provide bracketing for joins
New functionality in ON condition of joins
Number of tables which can participate in joins are now 50, earlier we can include only 9 tables in a join
Maximum no of subqueries has been also increased to 50 from 9
We can use USING CLIENT keyword instead of CLIENT SPECIFIED
Also Read: My First ABAP Program in S/4HANA
Q18. What are inline declarations in ABAP on HANA?
Ans: Inline declarations is a new way of declaring variables and field symbols at operand positions.
EXAMPLES:
Before 7.40
DATA text TYPE string.
text = `…`.
With 7.40
DATA(text) = `…`.
Declaration of table work areas
Before 7.40
DATA wa like LINE OF itab.
LOOP AT itab INTO wa.
...
ENDLOOP.
With 7.40
LOOP AT itab INTO DATA(wa).
...
ENDLOOP.
Declaration of a helper variable
Before 7.40
DATA cnt TYPE i.
FIND … IN … MATCH COUNT cnt.
With 7.40
FIND … IN … MATCH COUNT DATA(cnt).
Declaration of a result
Before 7.40
DATA xml TYPE xstring.
CALL TRANSFORMATION … RESULT XML xml.
With 7.40
CALL TRANSFORMATION … RESULT XML DATA(xml).
Declaration of actual parameters
Before 7.40
DATA a1 TYPE …
DATA a2 TYPE …
oref->meth( IMPORTING p1 = a1
IMPORTING p2 = a2
… )
With 7.40
oref->meth( IMPORTING p1 = DATA(a1)
IMPORTING p2 = DATA(a2)
… ).
Declaration of reference variables for factory methods
Before 7.40
DATA ixml TYPE REF TO if_ixml.
DATA stream_factory TYPE REF TO if_ixml_stream_factory.
DATA document TYPE REF TO if_ixml_document.
ixml = cl_ixml=>create( ).
stream_factory = ixml->create_stream_factory( ).
document = ixml->create_document( ).
With 7.40
DATA(ixml) = cl_ixml=>create( ).
DATA(stream_factory) = ixml->create_stream_factory( ).
DATA(document) = ixml->create_document( ).
Field Symbols
For field symbols there is the new declaration operator FIELD-SYMBOL(…) that you can use at exactly three declaration positions.
ASSIGN … TO FIELD-SYMBOL(<fs>).
LOOP AT itab ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<line>).
…
ENDLOOP.
READ TABLE itab ASSIGNING FIELD-SYMBOL(<line>) …
TYPES t_itab TYPE TABLE OF i WITH EMPTY KEY.
DATA(itab) = VALUE t_itab( ( 1 ) ( 2 ) ( 3 ) ).
Q19. When do you use “GROUPBY” clause in HANA SQL statements?
Ans: while using aggregate functions in a SELECT QUERY, all the columns that do not belong to aggregate-functions should be put in GROUP BY Clause.
Q20. What is the significance of “HAVING” clause in SQL statement?
Ans: In order to apply further filter for the aggregation function, HAVING clause can be used in the SELECT statement which is used with GROUPBY clause being mandatory. Eg. It is like applying where condition on the aggregated column.
When an aggregation is used with CASE statement, it has to be mentioned in the GROUPBY clause
Q21. What is the symbol to do “concatenation” operation in NW ABAP 7.4 ?
Ans. Pipe Symbol - |
Q22. What is constructor expression in NW ABAP 7.4?
Ans. It is used to create a Table in ABAP by specifying symbol #
Ex:
struct2 = CORRESPONDING #( struct1 ).
itab = VALUE #( ( 1 ) ( 2 ) ( 3 ) ).
Q23. What is the transaction code to check Schema name?
Ans. DBACOCKPIT
Q24. Can multiple ABAP systems connect to ABAP Database?
Ans. Yes. HANA 1.0 SP09 onwards
Q25. What is a Catalog in SAP HANA?
Ans. A Catalog is collection of Database Schemas in HANA. Schema: grouping of all database objects, Schema is a mandatory database object allows companies to use same database keeping data from multiple system where DCL and DB constraints can be managed at schema level
Q26. What is difference between SAP User and DB user?
Ans. Schema user , i.e the database user is used to access the data with certain authorization levels.
Q27. What is Information Model and why is it required?
Ans. Information Model: main purpose is to hide the technicalities to select data and make it easier for business users to model their data which can be pulled w/o technical knowledge just db functional knowledge is sufficient.
An information model: ( purpose was to hide the complexity and to overcome some setbacks with the queries )
Used to convert linear structure to a multi dimension structure w/o knowing technical language.
Are Process of converting source data (in tables) into business understandable format.
They also make use of Hardware advancements in HANA.
If we define information models inside HANA DB, We can also reduce the data transfer b/w DB and App layer.
Complex logic as well as transformation executed in DB layer.
Also Read: View the S/4HANA Views from Different Angles
Q28. What are different types of views in HANA?
Ans. 1. Attribute view
2. Analytic view
3. Calculation View
4. Decision Table
For the purpose of taking business informed decisions and they run on top of HANA DB doing code-pushdown or functional pushdown to the DB layer
Q29. What is the function of SQL optimizer?
Ans. SQL optimizer function is to process and optimize the SQL queries submitted to HANA and finally executed by the SQL engine in SAP HANA
Q30. What are the other three engines which are part of SAP HANA?
Ans. Calculation Engine: index-server architecture: procedural logic
Join Engine: regular SQL using joins
OLAP Engine: aggregation
Q31. Processing of models in the engine?
Ans.
Q32. What are different techniques of creating a Calculation view?
Ans. Graphical Editor and SQL Script Editor
Q33. What is a Star Schema in ABAP on HANA?
Ans. When we combine data of dimension (master) with measure (transaction), it becomes Star Schema. And to join two or more Star Schemas, it is done by Calculation View.
Q34. What is the limitation of Analytical view?
Ans. This view can have only one measure. It cannot have multiple measure. Basically one fact table in an Analytical view. Ideally only one Fact Table should only be used with Analytical view since Fact Table requires an aggregate.
Q35. what are steps to create an Attribute view?
Ans. Steps to create an attribute view in HANA Studio since graphical representation is not available in ABAP on Eclipse:
Name and description of attribute view
Table and Join
Hierarchies, Transformation, restricted and calculated columns
Save and Activate
Data Preview
Q36. what is the limitation of an Attribute view?
Ans. Attribute view cannot be used with aggregate functions.
Q37. What is Content in SAP HANA?
Ans. Content is collection of development packages where we add different development objects including Information Models: which are HANA specific data type.
Q38. What is a Package in SAP HANA?
Ans. It provides a name space for your development object. Once an information model is activated, it creates a view in the HANA DB and it is stored inside the schema.
Eg. <packagename>::<viewName> schema
It allows you to transport all logically related development objects. Grouping development artefacts together known as Delivery Unit.
Q39. Why Fact Table should not be added in an Attribute View?
Ans. It is recommended to use an Attribute View with only Master Table because of performance criteria. It is advisable that Fact/Transaction Table used with Analytical view, and not be used with Attribute view due to performance implication since Attribute View is processed in the join Engine of SAP HANA, it is not processed by OLAP Engine which is equipped to do aggregation.
Statement: To expose a View/Model to the user, you create a select query on top of your view and create an OData on your query and create a fiori app to expose it to the user…sap.viz OR use ALV grid
Q40. What is View Proxy in ABAP?
Ans. View Proxy is used to pull the data from a view in ABAP. To expose a Data Model to the application layer ( ABAP Layer ), SAP NW7.4 SP02 onwards, provides a feature called View Proxy which allows SAP HANA data models to communicate with the ABAP Layer using ADT in eclipse and lock the objects in a Delivery unit to transport the objects.
Q41. What is Hierarchy?
And. Hierarchy is used to realize data based on relation of data characteristics.
Click on Semantics -> Hierarchy Tab ->
Two types of hierarchy
Level based hierarchy – Relation between master data w.r.t. groups, these groups can come from multiple tables.
Parent-child hierarch – the relation works as self-relation. In this the table has a relation with itself and mark one of the column as parent and another a child. E.g. manager employee relation.
Q42. What are different types of JOINS in SAP HANA?
Ans.
Q43. What is an Analytical View?
Ans. When a Fact table to be connected to multiple dimensions, we use analytical view. The Analytical views are built to perform complex Aggregations( SUM, MIN, MAX, AVG, COUNT ) on measure. These views are processed by OLAP engine in SAP HANA. They are used to build so called STAR schema. Also has capabilities to define calculated columns, restricted columns, filters, import parameters, complex conversions.
It is important that In an analytical view, we must mark attributes and measures at the end in semantic. Because an aggregation will be applied only on measure.
Q44. How do you achieve currency conversion in Analytical view?
Ans. Use calculated columns and define the semantics.
Q45. What are components of a View Scenario?
Q46. What is a Calculation View?
Ans. To include multiple facts as part of data model, we can go for calculation view, these views are processed by Calculation Engine in SAP HANA. They are suitable for more complex calculation. CVs can be created in two ways: Graphical and SQL Script ( to achieve parallelization). SQL scripting in Calculation view can be implemented in two ways: CE functions ( to get better performance ) or pure SQL
Q47. Define Calculation Engine Architecture?
Q48. What are CE functions?
Ans. SAP HANA Provides ready-made functions which are implemented inside Calculations engine and executed with in the engine with enhanced performance for common tasks like :
projection (selection of some columns)
Joins (connect two data object)
Selection ( where clause )
Join with a Fact Table
Selection of data from column table
Unions
Aggregations
CE_*
St. In case of CE functions the call/execution remains in the CE engine, where as in case of SQL Scripts, it has to go outside of the Caln Engine to SQL Script Optimizer to execute the function leading to a drop in performance.
Q49. What are the cases when can you use different views for different requirements?
Q50. What is an alternate to View proxy?
Ans. Alternate to View Proxy is CDS view due to synchronization of transport objects.
Q51. What is ADBC?
Ans. ADBC stands for ABAP Database Connectivity. It is used to run HANA related queries directly using ABAP code. ADBC APIs are available since NW 7.4 to call the queries using simplified interface.
ADBC can be used when:
Your system does not have ABAP ADT available, you cannot create proxy object.
When HANA DB running as Secondary DB (Side Car Scenario)
Q52. What is a Decision Table?
Ans. A Decision Table is used for planning scenarios, that allows business users to model business rules with less/no technical knowhow and apply the rules to see the results with read data.
2 types of DT
Decision table with update value: We can update the data of a specific column in SAP HANA by defining business rule.
Decision table with Return Value: In this we have the result as an additional updated column. (preferred for use business cases: not changing the actual data in the DB)
Once a decision table is activated, it creates a stored procedure in the DB
Q53. What is BRMS System?
Ans. A Business Rule Management system manages set of rules which are frequently changing in the business.
Q54. Syntax to call a PROCEDURE in HANA?
Ans. CALL “<procedure_name>”(?)
Q55. What is the difference between Procedural (Scripting ) Vs Programming Language?
Ans. Programming language are independent products, they generate their own executables. Code is compiled by programming language and converted to machine code / OS code.
Eg: Compile a .java file it create a .class
Scripting languages are embedded on programming language. They rely on the APIs of programming language.
In SAP HANA, we have SQL scripting which is a Procedural Language.
Q56. What are the disadvantages of using Views?
Ans.
Cannot debug a views
Decomposing complex business logic, Intermediate results from the views cannot be store.
No possibility to express business logic – if, else, case, looping
SQL queries can only return one value and has no chaining.
Imperative logic.
Q57. What is SQL Script in HANA?
Ans. SQL script is a collection of extension to SQL (DML, DDL, DQL, DCL)
Allows developer to write performance-intensive logic inside database. One of the technique used in code-to-data paradigm.
Q58. How does the system process SQL script?
Also Read: New Age Open SQL
Q59. What are different type of Statements in SQL Logic?
Q60. On what all instances SAP HANA comes out of Parallelization mode?
Ans. Instances when HANA comes out of parallel mode:
“Select Statements” are executed in SAP HANA in parallel unless:
Local scalar parameters and variables are used in containers (procedure).
Read/write procedure or DDL/DML statements are execute (eg: CREATE, INSERT,UPDATE,MODIFY).
Imperative Logic is used (IF, CASE, LOOP)
SQL statements which are not assigned to variable. ( Eg: Lt_Anubhav = select * from snwd_pd where price > 1000; --Query 1 )
Q61. What are different types of SQL Scripts?
Q62. What are advantages of SQL script?
Ans.
SQL Script is executed and processed in the calculation engine within the HANA database.
SQL Script is able to perform complex calculations.
In SQL Script, a local variable can be declared to hold the interim result.
SQL Script Procedure can return more result by using "OUTPUT Parameter" while Normal SQL Procedure can return only one.
In SQL Script, you can define global or local tables types which can be used as parameters.
Q63. What are different Data Types in SAP HANA?
Ans. Different Data Types that are called Primitive Data Types in HANA are:
Numeric : TINYINT, SMALLINT, INT, BIGINT, DECIMAL, SMALL-DECIMAL, DOUBLE
Characters: VARCHAR, NVARCHAR, ALPHANUM
Data/time : TIMESTAMP, DATETIME
Binary type: VARBINARY
Large obj: CLOB, BLOB, NLOB
Q64. What are Containers in SAP HANA?
Ans. Containers are the blocks in which we write the Imperative or Declarative logic.
Q65. What are different types of Blocks ( Containers ) in SAP HANA?
Ans.
Q66. What is the difference between PROCEDURES and USER DEFINED FUNCTIONS in HANA?
Ans.
Also Read: SQL Script and HANA Stored Procedures
Q67. How do you declare variables in SQL script?
Ans. When we declare variable in SAP HANA SQL Script ( Scalar Parameters ), These variables are initialized with NULL value. We can explicitly assign value during creation also.
When we want to use a variable in SQL script, we use symbol colon (:) to refer the variable. E.g.
Declare x integer;
😡 should be used to refer value of x.
When we want to assign value to x, we don’t use colon (:) x
SQL script is case-insensitive
Every SQL script statement must end with semi-colon (;)
Q68. Syntax to declare Scalar Variable?
Ans. DECLARE <vname> <vtype> = <default_value>;
Q69. Syntax to Declare an Anonymous Block?
Ans. DO (in pname ptype => ?, out pname ptype => ?)
BEGIN
….
END;
Q70. What is advantage of procedure over anonymous block?
Procedure are pre-compiled containers with name.
We can call procedure from another procedure.
Q71. Syntax to create a Procedure and Call a Procedure?
Ans. CREATE PROCEDURE <proc_name> (in pname ptype, out pname ptype, inout pname ptype)
LANGUAGE SQLSCRIPT/R
DEFAULT SCHEMA <schema> READS SQL DATA
WITH ENCRYPTION AS
BEGIN
----code
END;
CALL <procname>(params);
Q72. What does DROP PROCEDURE in SQL do?
Ans. Whenever a New Procedure is created, in order to re-create or replace the existing procedure, it needs to be dropped first. Syntax to Drop Procedure:
DROP PROCEDURE <proname>.
Q73. What are different syntaxes in SQL script for different functionalities?
Ans. If condition
IF <cond> THEN
…..
ELSE IF <cond> THEN
….
END IF;
Loops – iteration
While Loop
While <condition> DO
END WHILE;
BREAK;
2. For loop
FOR i IN startIndex..EndIndex DO
….
END FOR;
Q74. What does “READ SQL DATA” do?
Ans. It tells the system to enter into Parallelization mode.
Q75. How to define EXCEPTION in SQL?
Ans. TRY.
…..code…
…...code…
CATCH ex_class INTO lx_obj.
…
ENDTRY.
Syntax:
DECLARE EXIT HANDLER FOR
1. SQLEXCEPTION –generic exception case
2. SQL_ERROR_CODE <codeno>
---code
END;
Also Read: Open SQL, CDS or AMDP? What technique to use?
Q76. What is the range of Custom Exceptions Error Code?
Ans. 10000 ~ 19999
Syntax:
SIGNAL SQL_ERROR_CODE 10000 SET message_text = ‘xyz’;
Q77. What are Cursors in HANA Database?
Ans. Whenever we want to work with multiple records in DB,
Load all data records in a table parameters, manipulate using table
Cursor – Process records directly from DB table Line By Line
Cursors are used to fetch data records from table row-by-row from result of a query assigned to cursor. We always bind a Query to cursor. It is also possible to parameterize cursor.
NOTE!!: If possible Avoid using Cursors in HANA DB , since HANA cannot optimize or run SQL in Parallel mode.
Q78. What steps to process a Cursor?
Declare a cursor and assign to query
DECLARE CURSOR(<params>) <Name> FOR <select>
Open the Cursor (Submit the query to Database) – query submitted to DB and data is loaded
in context area (memory)
OPEN <cursor name>
3. Fetch statement to process/manipulate the data one by one record.
FETCH <cursor_name> INTO <record>;
4. To access values of fields use: <record>.column_name
5. Close cursor
Q79. Syntax to create a Table Type?
Ans. Table types are created to hold multiple columns of different types
CREATE TABLE TYPE <tabtypename>( col type, col2 type);
CREATE TYPE <tabtypename> AS TABLE( col type, col2 type);
Pname TABLE(col type, col2 type….);
Q80. What is the syntax to create an Array?
Ans. An Array is a Single column table a one dimension structure to hold multiple values of same type. An Array CANNOT be used in SIGNATURE of a PROCEDURE.
DECLARE <array_name> < va_type> ARRAY = ARRAY(val1, val2,…)
Q81. What is use of UNNEST Function?
Ans. UNNEST function is used to convert one or many arrays into a table.
Syntax: Table_variable = UNNEST(:array_var) AS (column_name)
Q82. What are User Defined Functions in SAP HANA?
Ans. User Defined Functions in SAP HANA are the read only function that means we cannot perform any DDL and DML(insert update and delete) operation inside the body of the function.
Q83. What are different types of UDFs ( User Defined Functions ) ?
Q84. Things to consider while working with SQL Script Procedures for CODE Pushdown?
Ans.
Consider client handling while applying any aggregation on data
Since there is no explicit functionality of LUW concept in HANA, it has to be taken care while using SQL scripting
There is no implicit locking mechanism, it has to be taken care while working with SQL scripting on DB
Q85. What are disadvantages of using ADBC to CALL PROCEDURE?
Complex coding using SQL interface
No syntax check at design time.
Q86. What is bottom-up approach in HANA DB while creating proxy?
Ans. Whenever an Information Model or a Procedure is created in HANA DB, a View Proxy or Procedure Proxy is created in ABAP Stack respectively. Which means that an object already exists in a DB and in order to communicate with the DB object from ABAP stack, you need to create a proxy.
Q87. What is the disadvantage of using Proxies?
Ans.
Lifecycle management of HANA vs ABAP object.
No Access Control of Procedure
No extensibility
Also Read: AMDP in S/4HANA
Q88. What is AMDP ( ABAP Managed Data Procedures)?
Ans. This approach is called top-down approach where a procedure is created in ABAP stack NW 7.4 SP05 which acts like Master for editing , activating and transporting ( life-cycle) for the procedure object. When it is called for the 1st time corresponding HANA DB procedure gets created to support code-to-data paradigm or code-pushdown to HANA DB.
Q89. What are points to be considered while using AMDP?
A standard ABAP class (SE24), method used as container for AMDP.
SQL script code which was earlier done in HANA DB is added to this method
When we call the AMDP first time, it will create the corresponding DB procedure. Name of that procedure will be classname=>method
These methods are always called as static method.
It allows to handle runtime error. CX_AMDP_ERROR
It will be created in your schema which used for ABAP
When you call the AMDP, it calls the corresponding HANA DB procedure.
Q90. What are pre-requisites before using an AMDP?
Ans. Pre-requisites:
We must add an interface to a class in ABAP to make it powerful so that it can become a AMDP, IF_AMDP_MARKER_HDB
An ABAP method parameters has to be passed by Value.
All the parameters of AMDP has to be table type or scalar parameters, No object or nested tables allowed.
Methods with Returning parameter cannot be used as AMDP.
Q91. what are advantages & dis-advantages of using AMDP?
Advantages:
Syntax check
Lifecycle management is completely controlled by ABAP system.
Disadvantage:
Client handling
Locking and LUW
Q92. What is the syntax to create AMDP in a class-method?
METHOD method_name BY DATABASE PROCEDURE
FOR db_name(HDB) LANGUAGE sqlscript OPTIONS READ-ONLY
USING dbtab1 dbtab2 amdpname.
…..
….
…
ENDMETHOD.
Also Read: Core Data Services for HANA Beginners
Q93. What is CDS View?
Ans. CDS view is basically an abstraction of ABAP to Database layer which allows you to model semantic rich data models ( like Information views on HANA DB ) on ABAP Stack and on activation it leads to creation of corresponding Database View in DB. It is an enhancement of SQL which provides us DDL for defining semantically rich data models (table/view) and user define types in Database. It is an extension of SQL : i.e DDL DQL and DCL
St. The objective behind creating CDS Data Model is that , it will be understood by all SAP products viz SAP Fiori, KPI modeler, BO/BI, BOPF, FPM, IDA Native HANA Apps.
Q94. What is SQL enhancement ( CDS ) ?
Annotation to enrich the data models with additional details (all annotations starts with symbol @)
DB Entities are connected using Association at conceptual level (replacement of join conditions)
Expressions – used to code calculation in queries
Q95. What are different types of CDS?
1. ABAP CDS
2. HANA CDS
Q96. How to Define a CDS view?
Ans. CDS view is defined using CDS data definitions.:-> Also known as CDS document or CDS source code. To create CDS views we need to use ADT.
On activation it creates a CDS SQL view ( SE11 ) and a CDS entity
Q97. What are Annotations in CDS?
Ans. Annotations are used to add metadata information to CDS entity. Annotation specifies the properties and semantics of entity and its behavior when it is consumed. There are UI Annotations, Object Model annotations, VDM annotations, Environment Annotation etc.
Q98. What is the difference between CDS views and Traditional views?
Q99. What are two categories of CDS?
Ans. CDS with parameters and CDS without parameters
Q100. From semantic point of view of S/4 HANA what are the categories of CDS views?
Ans.
Also Read: Associations in S/4HANA
Q101. What is the concept of Association?
Ans. It represents join where the two columns are used in join where one of the column is a Projection. To make it available in the Data Preview, it has to be exposed to the DB. In S/4 HANA the association is indicated with a name starting underscore. Eg. _Supplier, _BusinessPartner etc.
Q102. What is Projection in CDS?
Ans. Columns are indicated using a Projection of a table, We can use $projection in CDS for the same in association join condition.
Q103. Techniques to Expose CDS to OData based on NW version ?
Q104. How to create an ALV report in SAP HANA using CDS view?
Ans. SAP NW 7.4 onwards ABAP list viewer comes with an IDA ( Integrated Data Access )
Advantage of Using ALV with IDA:
Only Selected Columns will be fetched from the DB
it is possible for tables that contain very large quantities of data to be displayed on the UI which is called Pagination and
Automatic Query (No need to write a SELECT Statement, since the IDA framework prepares the Query, sends it to the DB, pulls the data and displays it in the ALV. Only Data Source Name needs to be provided to the IDA f/w, this data source can be a CDS View, which leverages the strength of CDS like code pushdown and performance). The results of operations such as sorting, grouping, or filtering are also delivered with a very fast response time.
CLASS NAME: CL_SALV_GUI_TABLE_IDA=>CREATE_FOR_CDS_VIEW().
Also Read: IDA (Integrated Data Access) in HANA
Q105. What is the purpose of Cloud Connector?
Ans. In order to consume the OData service based on CDS, to create a Fiori app, we used concept of Cloud Connector. To communicate securely, over the internet , by S/4 HANA On-premise with the SAP Cloud Platform, we need Cloud Connector.
Q106. What are the steps to configure Cloud Connector?
1. setup your HANA Cloud Platform Trial - SCP hcp.sap.com
2. download msi
https://tools.hana.ondemand.com/#cloud
3. install microsoft 2013 VC++ distributable in CAL server
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=40784
3. login to sap cc -
access via https://localhost:8443/
user: Administrator/manage
4. add cloud sub account, hcp user password
expose resources
user linux exernal ip with port 50000 protocol http
5. Create handshake between OP and HCC
6. create destination
no authentication, on premise
client, webideenabled, system, usage
Q107. What are advantages of CDS views over AMDP?
Ans.
Reusability of database artefact.
Advanced Features such as Associations and Annotations.
Client handling can be achieved in CDS.
Q108. What is a CDS entity?
Ans. A CDS entity is enriched by annotations which are used to build end-to-end fiori app utilizing these annotations. To consume a CDS view, instead of consuming it in ABAP program it is advisable to consume it using “CDS entity” since it allows access to metadata.
Q109. What is the purpose of UI Annotations in CDS view?
Ans. In order to Develop CDS view for Analytical tools for BW, VDM – Virtual Data Model – Analytical query can be build using CDS views.
An Analytical App can be build using a CDS view ( Consumption View ) on top of a simple CDS view ( interface view) using UI annotations.
Using UI annotations, we can define selection fields, the lines items of table, data points of chart, measures and dimensions for chart and expose this CDS as an odata service and build a Fiori App
Q110. What is CDS Table Function?
Ans. CDS Table Function can only be implemented with NetWeaver 7.5 which calls an AMDP ( ABAP Managed Data Procedure) using CDS view. Using CDS interface concept, underlying calls an AMDP.
This is required in case there is some functionality which CDS cannot achieve -> Eg. Data Type Mismatch, Looping, Conditional Looping and Logic
Q111. How can you secure your Data Access using CDS view?
Ans. Right click -> Core Data Services Folder -> Create Access Control -> mention the PFCG Role Name
Q112. What are different UI annotation in CDS Views?
Ans.
Start with VDM Annotation : Define it as Consumption View
@UI.headerInfo – used to set the title of the table
@UI. presentationVariant – to initialize the UI ( available only on S/4 HANA systems ), define SORT order, group based on fields, define default visualization at the view level
Properties to be defined the fields in selection
@UI. selectionField – selection parameters
@UI.identification – to define label from a user point of view
@UI.lineItem – to define the position of the line item
@UI.chart -- need to mark @UI.dataPoint : { title: xyz }
@UI.dataPoint -- to specify a measure in the chart
Also Read: OData Service through Annotation
Q113. What is Full Text Search in SAP HANA?
Ans.
To enable Full Text search – there has to be a FULLTEXT index that needs to be present in the Table, which is a DB specific feature.
Syntax: CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX <indextextvariable> on <table_name(field)> FAST PREPROCESSOR OFF;
Q114. What does FAST PREPROCESSOR keyword Indicate?
Ans. HANA does pre-processing to enable searches which are case-sensitive.
It achieves this using following techniques:
Normalization : converting each letter into its equivalent upper and lower care.
Tokenization : breaking every statement into words
It also does linguistic analysis of words: finding equivalent word with the nearest meaning
Q115. What is FUZZY search in SAP HANA?
Ans. FUZZY SEARCH in SAP HANA is a Fault Tolerant search which allows a level of accuracy ( which can be specified in the WHERE clause as percentage ) , and returns the value with an approximate match.
Ex: Query
Result:
Comments
Post a Comment